snAPI.Constants module#
- class snAPI.Constants.DeviceType#
Bases:
EnumSnAPI doesn’t only support real Harp devices. It is also possible to use ptu-files that act as a hardware-like device.
- Undefined = -1#
This is for internal use only.
- HW = 0#
This is a real device, for instance a MultiHarp.
- File = 1#
This is a file device. That means a ptu file treated as a device.
- class snAPI.Constants.MeasMode#
Bases:
EnumThe PicoQuant TCSPC devices support different measurement modes. The constants defined here are specified by the measurement mode with which the device gets initialized when using
snAPI.initDevice.In histogram mode, the photon arrival time data is instantly processed to calculate the time differences between sync events and events on the input channels. These then get accumulated in a set of histograms, one for each input channel. This is typically used for classic fluorescence lifetime measurements and requires very little data processing effort by the user. As opposed to this, the time tagging modes T2 and T3 are designed to stream the raw photon arrival time data to the host PC where the data then can be processed and analyzed. This allows more flexibility to facilitate a huge range of more advanced applications. Data processing can be carried out directly “on the fly” while the measurement is running. Alternatively the data can be streamed to a file or PC memory and be processed later. The snAPI library supports both approaches.
- Histogram = 0#
Histogram Mode
For the measurement class
Histogramit is useful to initialize the device in Histogram mode. For devices that support hardware histogramming. This will enable higher count rates than software processing of the raw stream of time tags.Note
In histogram mode no data is written to disc because the raw data stream is processed internally and does not get transmitted to the API.
- T2 = 2#
T2 mode
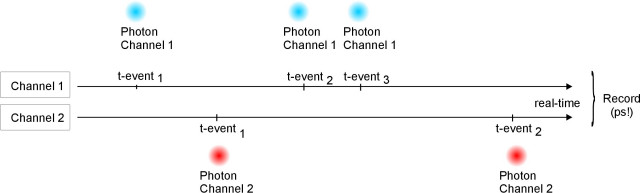
The T2 mode is PicoQuants time-tagging mode. In T2 mode, no periodic sync signal is required. The sync input can therefore be used to connect an additional photon detector. T2 mode is often used for any kind of coincidence detection, such as coincidence counting and correlation for, e.g., antibunching in a HBT set-up. Two pieces of information are collected for each event:
The elapsed time since the start of the measurement
The channel at which the event has been detected
- T3 = 3#
T3 Mode
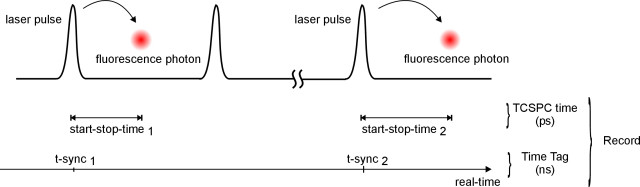
The T3 mode is an elegant solution for performing measurements at very high synchronization rates and can provide more effective data encoding for many applications. This mode is ideally suited for luminescence lifetime imaging and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Three different pieces of information are recorded for each detected event:
The start-stop time difference (similar to classic TCSPC)
The number of elapsed sync pulses since measure ment start
The channel at which the event has been detected
- class snAPI.Constants.MeasControl#
Bases:
EnumThis constant is for software or hardware starting and stopping (triggered) measurements. It is also necessary to set this for using White Rabbit. See
Device.setMeasControl.- SingleShotCTC = 0#
Supported devices [MH150/160 | HH400 | TH260 | PH330 | HH500]
Acquisition starts by software command and runs until CTC expires. The duration is set by the aqcTime parameter (>0). SwStartSwStop is in use if aqcTime parameter is 0.
- C1Gated = 1#
Supported devices [MH150/160 | HH400 | TH260 | PH330 | HH500]
Data is collected for the period where C1 is active. This can be the logical high or low period dependent on the value supplied to the parameter startEdge.
- C1StartCtcStop = 2#
Supported devices [MH150/160 | HH400 | TH260 | PH330 | HH500]
Data collection is started by a transition on C1 and stopped by expiration of the internal CTC. Which transition actually triggers the start is given by the value supplied to the parameter startEdge. The duration is set by the aqcTime parameter (>0).
- C1StartC2Stop = 3#
Supported devices [MH150/160 | HH400 | TH260 | PH330 | HH500]
Data collection is started by a transition on C1 and stopped by by a transition on C2. Which transitions actually trigger start and stop is given by the values supplied to the parameters startEdge and stopEdge.
- WrMaster2Slave = 4#
Supported devices [MH150/160 | HH500]
White Rabbit master to slave
- WrSlave2Master = 5#
Supported devices [MH150/160 | HH500]
White Rabbit slave to master
- SwStartSwStop = 6#
Supported devices [MH150/160 | PH330 | HH500]
Software start and software stop is automatically used if aqcTime ist set to 0 in a measurement.
- ContC1Gated = 7#
Supported devices [HH400 | HH500]
Warning
The continuous mode is currently not supported in snAPI.
- Cont_C1_Start_CTC_Stop = 8#
Supported devices [HH400 | HH500]
Warning
The continuous mode is currently not supported in snAPI.
- Cont_CTC_Restart = 9#
Supported devices [HH400 | HH500]
Warning
The continuous mode is currently not supported in snAPI.
- class snAPI.Constants.RefSource#
Bases:
EnumPicoQuant TCSPC devices can use their internal crystal clock but can be synchronized with an external reference clock as well. The latter is preferable when a clock drift between multiple instruments in an experiment needs to be avoided. The constants defined here specify the reference clock to use. See
snAPI.initDevice.- Internal = 0#
Supported devices [MH150/160 | HH400 | (TH260) | PH330 | HH500]
Internal clockThis is the default and normally selected by most users when only one device is being used.
- External_10MHZ = 1#
Supported devices [MH150/160 | HH400 | PH330 | HH500]
10MHz external clockThis is for use with an industry standard 10MHz reference such as an atomic clock or another Harp.
- Wr_Master_Generic = 2#
Supported devices [MH150/160 | HH500]
White Rabbit master with generic partner
- Wr_Slave_Generic = 3#
Supported devices [MH150/160 | HH500]
White Rabbit slave with generic partner
- Wr_Grandm_Generic = 4#
Supported devices [MH150/160 | HH500]
White Rabbit grand master with generic partner
- Extn_GPS_PPS = 5#
Supported devices [MH150/160 | HH500]
10 MHz + PPS from GPS
- Extn_GPS_PPS_UART = 6#
Supported devices [MH150/160 | HH500]
10 MHz + PPS + time via UART from GPS
- Wr_Master_Harp = 7#
Supported devices [MH150/160 | HH500]
White Rabbit master with the Harp as partner
- Wr_Slave_Harp = 8#
Supported devices [MH150/160 | HH500]
White Rabbit slave with the Harp as partner
- Wr_Grandm_Harp = 9#
Supported devices [MH150/160 | HH500]
White Rabbit grand master with the Harp as partner
- External_100MHZ = 10#
Supported devices [PH330]
100MHz external clock
- External_500MHZ = 11#
Supported devices [PH330]
500MHz external clock
- class snAPI.Constants.TrigMode#
Bases:
EnumThe PicoQuant TCSPC devices have different trigger modes. Some of them can switch between them. See
Device.setSyncTrigModeandDevice.setInputTrigMode.- Edge = 0#
This selects the edge trigger.
- CFD = 1#
This selects the CFD (Constant Fraction Discriminator) trigger
- class snAPI.Constants.LogLevel#
Bases:
EnumThis is for switching the different log levels on and off with
snAPI.setLogLevel().- Api = 0#
This logs API commands.
- Config = 1#
This logs the loading of
snAPI.setIniConfigand notifies you, if something goes wrong.
- DataFile = 3#
This logs loading and creating of th ptu file entries.
- Manipulators = 4#
This logs the creating, deleting and many more of the
Manipulators.
- class snAPI.Constants.CoincidenceMode#
Bases:
EnumThis defines the different coincidence modes. See
Manipulators.coincidence.- CountAll = 0#
This is the standard mode. Every new event can count as coincidence if it meets the conditions of the different channel count in the defined window time.
- CountOnce = 1#
This mode allows to count every new event only one time. If count it meets the conditions of the different channel count in the defined window time it will generate a coincidence count and get erased for the generation of further coincidences.
- class snAPI.Constants.CoincidenceTime#
Bases:
EnumThis defines the position of the timetag of the calculated coincidence. See
Manipulators.coincidence.- First = 0#
The coincidence will get the timetag of the first event that build the coincidence.
Note
This makes it is possible to create a herald filter with herald = coincidence and the same window time to filter (removing) the coincidences. It will work as anti coincidence than.
- Last = 1#
The coincidence will get the timetag of the last event that build the coincidence.
- Average = 2#
This builds the average of the timetags that builds the coincidence.
- class snAPI.Constants.WRmode#
Bases:
EnumThis configures the role of the device onto the White Rabbit network. See
WhiteRabbit.setMode.- Off = 0#
It configures the device to be not a member onto the White Rabbit network.
- Slave = 1#
This let the device synchronize its clock with a master.
- Master = 2#
It implements a controller function and sends the data onto the White Rabbit network. Only one Master is allowed on the White Rabbit network.
- Grandmaster = 3#
The device synchronizes its clock to an external reference signal and propagates precise timing to other devices on a White Rabbit network.
- class snAPI.Constants.WRstatus#
Bases:
EnumUse this function the get the status of the WR node. See
WhiteRabbit.getStatus.PTP: Precision Time Protocol
Servo is a feedback control mechanism. It continuously adjusts the local clock based on the error between two clocks.
- LinkON = 1#
WR link is switched on
- LinkUP = 2#
WR link is established
- ModeBitmask = 12#
mask for the mode bits
- ModeOff = 0#
mode is off
- ModeSlave = 4#
mode is slave
- ModeMaster = 8#
mode is master
- ModeGMaster = 12#
mode is grandmaster
- LockedCalibrated = 16#
locked and calibrated
- PtpBitmask = 224#
mask for the PTP bits
- PtpListening = 32#
waiting for packets
- PtpUncalibratedWRSlaveLock = 64#
slave is actively attempting to synchronize
- PtpSlave = 96#
Receives synchronization information from the master clock
- PtpMasterWRMasterLock = 128#
the White Rabbit node or switch operates as both a PTP master and a WR master, it is in a locked state
- PtpMaster = 160#
reference clock source for synchronization
- ServoBitmask = 1792#
mask for the servo bits
- ServoUninit = 256#
servo not initialized
- ServoSyncSec = 512#
servo seconds synchronization
- ServoSyncNSec = 768#
servo nano seconds synchronization
- ServoSyncPhase = 1024#
servo phase alignment process
- ServoWaitOffset = 1280#
servo control loop detects a significant offset between the local clock and the master clock.
- ServoTrackPhase = 1536#
servo actively adjusts clock frequencies to minimize phase discrepancies
- MacSet = 2048#
user defined mac address is set
- IsNew = 2147483648#
status updated since last check
- class snAPI.Constants.MeasSubMode#
Bases:
EnumThe PTU-File-Header contains numerous tags that describe the measurement configuration. These can be used for further analysis. For example, to use the PTU file with SymPhoTime 64 for FLIM analysis, the mandatory parameter Measurement_SubMode must be set to Image. Set this option with
snAPI.setMeasSubMode.- Default = 0#
Default
This is the default value and applies to all measurements that are not location-specific.
- Point = 1#
Point
Use this to indicate that the measurement refers to a single location.
- Line = 2#
Line
Use this to indicate that the measurement is being performed using line scanning.
- Image = 3#
Image
Use this to indicate that the measurement is being performed using image scanning. To analyze the data with SymPhoTime64 you have to set a lot of tags using the
snAPI.addIntTag. See also the Demo_Imaging_PTU.py

